Introduction to the Elevation Map of Europe
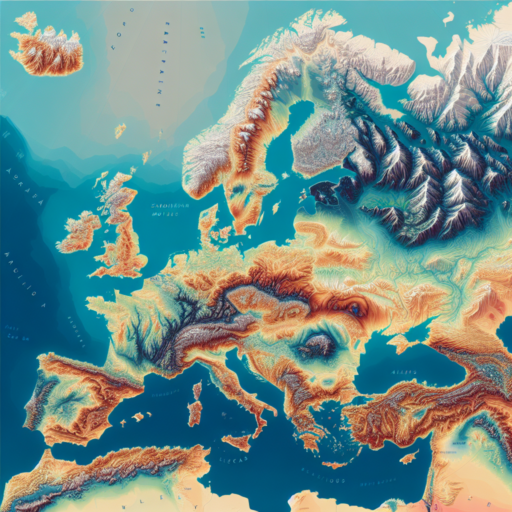
Europe’s diverse landscape is beautifully illustrated through its elevation map, depicting the continent’s vast array of mountains, plains, and valleys. Understanding the elevation map of Europe is essential for geographers, hikers, and anyone interested in the natural beauty and geographic diversity of this continent. This introduction aims to shed light on the significance of elevation variations across Europe and how they influence climate, biodiversity, and human settlements.
The elevation map of Europe reveals the contrast between the high-altitude areas, such as the Alps, Pyrenees, and the Scandinavian Mountains, and the lower plains found in regions like the Great European Plain. The significance of these elevation differences is not only geographical but also plays a crucial role in shaping the climate patterns, river systems, and agricultural landscapes across the continent. For instance, higher elevations tend to have cooler temperatures and more precipitation, which affects the types of vegetation and wildlife that can thrive in these areas.
Moreover, understanding Europe’s elevation map is pivotal for educational purposes and planning outdoor activities. It helps in identifying the best trails for hiking, understanding potential challenges in navigation, and appreciating the panoramic views offered by the continent’s varied topography. Whether you’re a student, a traveler, or a professional geographer, grasping the complexity and beauty of Europe’s elevation map enriches your knowledge and experience of the continent.
Understanding Europe’s Varied Terrain Through Elevation Maps
Europe’s geography presents a rich tapestry of landscapes, from the rolling plains of the east to the rugged mountains of the west. Through the lens of elevation maps, one gains a profound understanding of this diversity, showcasing Europe’s natural beauty and geographical complexities. Elevation maps, with their detailed depictions of height above sea level, transform abstract heights into a vivid mosaic of Europe’s varied terrain.
Elevation maps serve as a critical tool for understanding the relationship between human settlement patterns, agricultural practices, and the natural environment. For instance, the high altitude areas of the Alps and Pyrenees are less populated and have adapted different land use strategies compared to the fertile plains of the Loire Valley in France or the Danube River basin. These maps not only reveal the physical challenges posed by Europe’s landscapes but also highlight areas of significant ecological value and conservation.
The use of elevation maps facilitates in-depth analysis of climate variation across Europe as well. The stark difference in elevation between regions contributes to the wide range of climates experienced continent-wide. From the perpetually snow-capped peaks of Norway’s mountains to the warm, gentle slopes of the Mediterranean coast, elevation maps illustrate how altitude influences regional climates, impacting everything from biodiversity to the way of life of the inhabitants.
No se han encontrado productos.
Topographic Features of Europe Highlighted in Elevation Maps
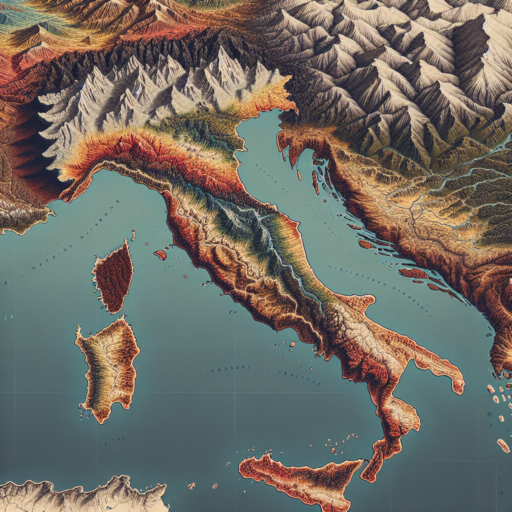
Elevation maps of Europe showcase a diverse terrain that ranges from vast plains to towering peaks, providing a detailed visualization of the continent’s topographic features. The representation on these maps highlights the natural contours and elevations, giving users an insight into the geographic diversity Europe holds. Among these features, the Alpine region, the Central European Plain, and the Scandinavian Mountains stand out for their distinctive characteristics and the varying climates they foster.
Alpine Region
The Alpine region, prominently featured in elevation maps, showcases Europe’s most significant mountain range. These maps highlight the range’s elevated terrains, displaying a gradient of colors to depict varying heights. The Alps play a crucial role in influencing Europe’s climate and weather patterns, acting as a natural barrier that affects precipitation distribution. The elevation maps also allow for the exploration of the Alpine rivers and valleys, illustrating how these features form unique ecological niches.
Central European Plain
In contrast to the rugged terrains of the Alps, the Central European Plain appears on elevation maps as a vast, gently sloping area that extends across several countries. This feature is crucial for understanding Europe’s agricultural capabilities, as the plain hosts a significant portion of the continent’s farmland. Through the use of shades and contours, the maps reveal the plain’s subtle topographic variations, emphasizing its importance not only for agriculture but also for human settlement and historical migrations.
Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains, stretching across the Scandinavian Peninsula, are another prominent feature captured by elevation maps. These maps showcase the mountain range’s steep slopes and high peaks, some of which reach deep into the Arctic Circle. The variation in elevation is depicted through a stark contrast between the highlands and the surrounding lowlands, highlighting the physical barriers these mountains create. This barrier effect is integral to understanding the distinct weather patterns and ecosystems observed in Northern Europe.
How to Read an Elevation Map of Europe
Reading an elevation map of Europe can seem daunting at first, but with a few tips, you can easily interpret the geography and topography of the continent. Elevation maps use colors, lines, and labels to represent the height above sea level and the shape of the land. Understanding these elements is key to reading the map accurately.
Understanding Elevation Colors
The most visually striking feature of an elevation map is its color scheme. Generally, warm colors like red and orange represent higher elevations, while cooler colors such as blue and green denote lower elevations. This color gradient helps in quickly identifying mountainous regions and plains. For instance, the Alps, a major mountain range stretching across eight countries in Europe, are often depicted in darker shades of brown and red, indicating their higher elevation.
Interpreting Contour Lines
Contour lines are another crucial element used to depict elevation on maps. These thin lines connect points of equal elevation. Close together lines indicate a steep slope, while lines that are spread out suggest a more gentle slope. By studying these patterns, you can visualize the shape of the terrain. For example, the gentle slopes of the rolling hills in the French countryside will have contour lines that are far apart, whereas the steep slopes of the Norwegian fjords will have closely spaced contour lines.
Remember, reading an elevation map of Europe effectively requires a bit of practice. By focusing on the map’s color gradients and paying close attention to the contour lines, you can gain a deep understanding of Europe’s diverse landscape. Whether you’re a geography student, a hiker planning your next trip, or simply a curious explorer, mastering the skill of reading elevation maps will enrich your knowledge and appreciation of the continent.
The Significance of Elevation in Europe’s Climate and Weather
The topography of Europe presents a varied tapestry of elevation, ranging from the majestic peaks of the Alps to the low-lying areas of the Netherlands. This significant variation in elevation plays a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s diverse climate and weather patterns. Elevation not only influences temperature gradients but also affects precipitation distribution and wind patterns across the continent.
Temperature Variations with Elevation: As one ascends through different elevation zones in Europe, noticeable changes in temperature become apparent. Higher altitudes, such as those found in mountainous regions, typically experience cooler temperatures year-round compared to lower elevations. This phenomenon, known scientifically as the lapse rate, impacts the overall climate in elevated areas, resulting in colder climates at the tops of mountains and warmer, more temperate conditions in the valleys and plains.
Impact on Precipitation: Elevation not only influences the thermal characteristics of an area but also plays a crucial role in determining its precipitation patterns. Mountain ranges, acting as natural barriers, intercept moisture-laden air masses, leading to increased precipitation on the windward side and creating rain shadow effects on the leeward side. This results in varied microclimates across Europe, from the wet, lush landscapes of the western Highlands to the arid, dry regions on the leeward sides of mountains.
Europe’s Highest and Lowest Points: Insights From Elevation Maps
Elevation maps of Europe reveal a diverse topography that stretches from the vast, icy expanses of the northern tundra to the sunny Mediterranean shores in the south. These maps highlight not just the geographical diversity but also pinpoint the continent’s highest and lowest points, offering unique insights into Europe’s natural wonders. Exploring these extremes provides a vivid picture of Europe’s physical landscape and the environmental factors that shape it.
Europe’s Summit: Mount Elbrus
Located in Russia, Mount Elbrus stands as Europe’s highest peak, reaching an impressive elevation of 5,642 meters (18,510 feet) above sea level. This dormant volcano, situated in the Caucasus Mountain range, is marked distinctly on elevation maps, signifying not only its physical prominence but also its significance to geographers and climbers alike. The mountain’s snowy peak, visible from great distances, attracts thousands of adventurers every year, each aiming to conquer Europe’s rooftop.
Below Sea Level: The Caspian Depression
Contrasting sharply with Europe’s lofty heights is the Caspian Depression, a low-lying flatland located below sea level in Kazakhstan and Russia. This region, reaching down to more than 28 meters below sea level, delineates Europe’s lowest geographical point. Elevation maps provide crucial insights into this area’s below-sea-level topography and its ecological importance. The Caspian Depression is not only an interesting geographical anomaly but also a vital habitat for a variety of plant and animal species.
Interactive Elevation Maps of Europe: A Tool for Explorers and Educators
Exploring the diverse terrain of Europe has never been easier, thanks to the emergence of interactive elevation maps. These digital marvels offer an immersive experience that caters not only to avid explorers but also serves as an invaluable resource for educators. By providing a detailed three-dimensional view of Europe’s topography, users can virtually traverse mountains, valleys, and plains, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the continent’s geographical diversity.
For explorers, these maps are a treasure trove of information, offering insights into challenging terrains and helping in planning expeditions with precision. The ability to zoom in and out and explore different altitudes can aid significantly in routing and preparing for the physical demands of the terrain. On the other hand, educators find these maps to be an engaging tool to bring geography lessons to life. Interactive elevation maps allow students to visually comprehend the scale and majesty of Europe’s landscapes, from the towering Alps to the vast Eurasian Steppe, enhancing their learning experience.
Moreover, the function of being interactive means that users are not just passive observers but active participants. They can select specific areas to study in detail, compare elevations, and even simulate climatic conditions at different altitudes. This interactive feature not only makes it easier to understand complex geographical concepts but also engages the user, making learning fun and memorable.
Comparing Elevation Maps: Europe vs. Other Continents
Understanding the Topographical Diversity
When comparing elevation maps, Europe presents a distinct contrast against other continents, primarily due to its topographical diversity. Europe’s landscape ranges from the vast lowland regions in the north to the rugged, mountainous regions in the south. This diversity is especially notable when compared to continents like Africa, which boasts the extensive Sahara Desert, and Asia, home to the planet’s highest peak, Mount Everest. Europe’s highest point, Mount Elbrus, while formidable, does not reach the extreme elevations found in Asia.
Key Elevation Features in Europe
- The Alps: Spanning across multiple countries, the Alps are Europe’s major mountain range, offering a stark contrast to the relatively flat terrains of Eastern Europe.
- The Scandinavian Mountains: These mountains run through the Scandinavian Peninsula, comparing modestly to the Rockies in North America in terms of elevation and ruggedness.
- The Great European Plain: Representing one of the most extensive lowland areas, it starkly contrasts with South America’s Andes, the longest continental mountain range in the world.
Elevation Extremes: Europe vs. Other Continents
Europe’s elevation extremes are quite mild compared to the soaring heights and deep basins found on other continents. For instance, the difference in elevation within Europe is less pronounced than in South America, where the Andes reach monumental heights, and Asia’s profound depth at the Dead Sea. Such comparisons highlight Europe’s unique position, lying mostly at moderate elevations, which, in turn, has influenced its climate, biodiversity, and human activities throughout history.
Practical Applications of Elevation Maps in Planning Trips Across Europe
Utilizing elevation maps for planning trips across Europe presents a unique approach in preparing for diverse landscapes and challenges. These maps not only provide insights into the terrain but also empower travelers with the ability to anticipate the physical demands of their journey. From the steep inclines of the Alps to the gentle roll of the hills in the Tuscan countryside, elevation maps offer a detailed preview of what to expect, enabling better preparedness for hiking, cycling, or even road tripping across this varied continent.
Elevation maps are particularly useful in identifying routes that match the fitness levels and preferences of travelers. For instance, those seeking a less strenuous experience can pinpoint paths with minimal elevation changes, ensuring a more comfortable and accessible trip. Conversely, adventure enthusiasts can seek out challenging routes, leveraging the detailed topographical information to plan for climbs, descents, and the breathtaking views that come as a reward for their efforts. This strategic use of elevation data enhances the trip planning process, tailoring the European adventure to personal capabilities and goals.
Beyond physical preparation, elevation maps serve a critical role in logistical and safety planning. They can signal potential weather changes that come with different altitudes, guide accommodation choices based on scenic preferences or necessity, and provide crucial data for emergency planning and response strategies. The utility of elevation maps in planning trips across Europe is thus multifaceted, combining the joy of discovery with the reassurance of being well-prepared for the journey ahead.
Future Trends in Mapping Europe’s Elevation: Technological Advances
Exploring the next wave of technological innovations, the future of mapping Europe’s elevation is poised for significant transformations. As geospatial technologies evolve, they promise to offer unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in capturing the continent’s diverse topography. This evolution is not only crucial for scientific research but also plays a pivotal role in planning and development endeavors across various sectors.
Leveraging LiDAR Technology
The advent of Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology has been a game-changer in the realm of elevation mapping. With its ability to generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics, LiDAR stands at the forefront of the technological advances shaping Europe’s elevation mapping future. Its application is increasingly becoming more widespread, enhancing both natural and urban landscape surveys.
Integration of Drone Technology
Another significant technological stride is the integration of drone technology into elevation mapping practices. Drones offer a nimble and highly effective means of data collection, capable of accessing remote or challenging terrain with ease. This capability is particularly advantageous for mapping the intricate elevations of Europe’s vast landscapes, from the rolling hills of the countryside to the cragged cliffs of coastal regions. Drones not only streamline data collection but also reduce the time and costs associated with traditional surveying methods.
Advancements in Satellite Imagery
The enhancement of satellite imagery technologies continues to refine elevation mapping processes. With satellites capable of capturing high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, the scope for detailed and accurate elevation data is expanding. This improvement is instrumental in mapping Europe’s elevation, offering a comprehensive overview that aids in environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster management. Satellite imagery, combined with other geospatial data, is setting a new standard for mapping precision and reliability.