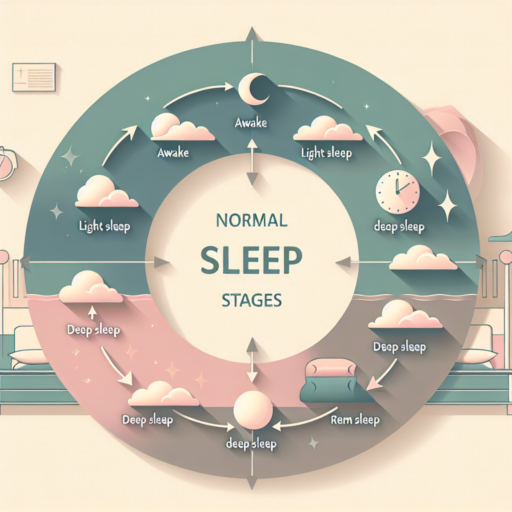
What are the 5 types of sleep?
No se han encontrado productos.
What is REM sleep vs deep sleep?
When we discuss sleep, it’s essential to understand the distinctions between REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep and deep sleep, as both play vital roles in our overall health and well-being. REM sleep is perhaps best known for being the stage of sleep where most of our dreaming occurs. During REM sleep, brain activity increases, mirroring the activity during waking hours. This stage is crucial for cognitive functions such as memory consolidation and mood regulation.
In contrast, deep sleep, or slow-wave sleep, is the most restorative phase of sleep. During deep sleep, our brain waves slow down, and the body focuses on healing and growth. This stage is particularly important for physical recovery, immune function, and energy restoration. It’s during deep sleep that the body releases growth hormones, repairs tissues, and strengthens the immune system.
Distinguishing REM sleep from deep sleep is not just a matter of understanding our sleep patterns; it’s about recognizing the balance needed between these stages for optimal health. While REM sleep supports our brain’s ability to learn and create new memories, deep sleep is indispensable for physical health and recovery. A healthy sleep cycle will typically cycle through stages of light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep several times throughout the night, with longer periods of REM sleep occurring towards the morning.
What is the best type of sleep?
The best type of sleep, often referred to as restorative sleep, plays a critical role in our health and well-being. This phase of sleep, primarily encompassed by deep sleep and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, is crucial for physical recovery, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation. Understanding how to optimize our sleep to enhance these stages can profoundly impact our overall health.
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is especially beneficial for physical health. During this stage, the body focuses on repairing tissues, strengthening the immune system, and regenerating cells. Achieving sufficient deep sleep helps to ensure these vital processes are carried out effectively. Techniques to increase deep sleep include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful environment free from disruptions.
Furthermore, REM sleep, which stands for Rapid Eye Movement sleep, is paramount for cognitive functions and emotional health. It is during REM sleep that the brain processes emotions and memories, integrating new information with established knowledge. Enhancing REM sleep can be facilitated by reducing stress before bedtime, avoiding caffeine and alcohol close to sleep time, and ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment.
Practical Tips to Improve Sleep Quality
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule to synchronize your body’s internal clock.
- Ensure your sleeping environment is dark, quiet, and cool to promote uninterrupted sleep.
- Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime to enhance the quality of REM sleep.
What is stage 4 of sleep?
Stage 4 of sleep, also known as deep sleep or delta sleep, is a critical part of the human sleep cycle. This stage is where the body achieves its most restorative and rejuvenating sleep. During this time, the brain begins to produce slow, deep delta waves, indicating a state of deep rest.
One of the core functions of stage 4 sleep is physical restoration. In this phase, the body repairs muscle tissue, stimulates growth and development, boosts immune function, and restores energy. It’s a period where the body focuses on recovery and health, making it essential for overall wellbeing.
This stage of sleep is also crucial for cognitive functions and emotional health. It helps in consolidating memories, processing emotions, and relieving stress and anxiety. Lack of sufficient deep sleep can lead to impaired memory, increased stress levels, and decreased cognitive capabilities over time.