Understanding Deep Sleep and Its Importance
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is a crucial phase in our sleep cycle that plays a significant role in our overall health and well-being. During deep sleep, our brain waves slow down, and our bodies focus on repair and rejuvenation. This stage of sleep is paramount for memory consolidation, where the brain processes and stores new information, making it essential for learning and memory retention. Furthermore, deep sleep aids in the recovery of the body, repairing tissues, and strengthening the immune system, which is vital for fighting off illnesses and maintaining optimal health.
One of the key benefits of deep sleep is its impact on physical health. Studies have shown that adequate deep sleep can help regulate hormone levels, including those responsible for growth and appetite. This regulation can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing obesity-related illnesses. Additionally, during deep sleep, the body releases growth hormones that contribute to muscle development and tissue growth, making this sleep phase especially crucial for athletes or individuals recovering from injuries.
Mental health also greatly benefits from deep sleep. The mind uses this time to relax and rejuvenate, lowering stress and anxiety levels. It’s during this quiet but crucial phase that our emotional health is fine-tuned, and our cognitive functions are enhanced. Without sufficient deep sleep, individuals may experience mood swings, increased stress, and difficulties in concentration and decision-making. Thus, ensuring an ample amount of deep sleep is key to maintaining not only physical but also mental health stability.
What Is Deep Sleep and What Role Does It Play in Your Health?
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is a critical phase in our sleep cycle that allows our bodies and minds to rejuvenate. During this stage, your body goes into a state of deep relaxation, where your heartbeat, breathing, and brainwave activity slow down. It’s a period of restorative sleep that is essential for various health aspects, including physical recovery, cognitive function, and emotional well-being.
The Physical Benefits of Deep Sleep
One of the primary roles of deep sleep is physical repair and regeneration. During this phase, your body releases growth hormones, which facilitate cell repair and growth. This process is vital for muscle recovery, tissue growth, and strengthening the immune system. Consequently, getting adequate deep sleep can help mitigate the risk of chronic diseases, improve physical performance, and maintain a healthy weight.
Cognitive and Emotional Health
Deep sleep also plays a pivotal role in cognitive functions and emotional health. It helps in consolidating memories, making it easier for the brain to store and retrieve information. Moreover, deep sleep regulates the levels of neurotransmitters that affect mood, stress, and anxiety. Ensuring sufficient deep sleep can enhance brain function, improve mood, and decrease the likelihood of developing mental health issues.
Overall, understanding the significance of deep sleep and its impact on health can motivate individuals to adopt better sleep habits. Ensuring a stable sleep schedule, reducing exposure to screens before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can contribute to achieving the restorative benefits of deep sleep.
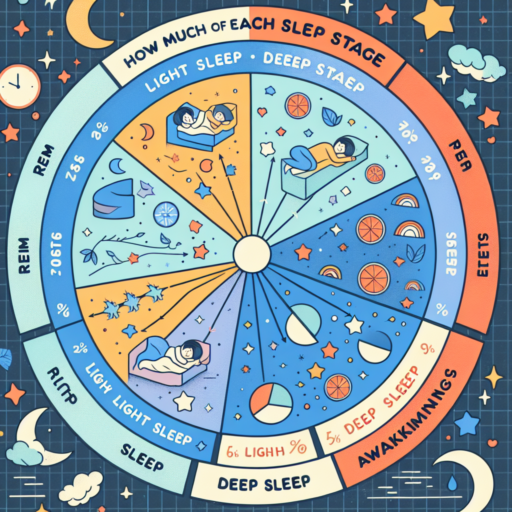
Normal Deep Sleep Percentages by Age Group
Understanding normal deep sleep percentages by age group is crucial for assessing the quality of sleep one is getting. Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, plays a pivotal role in overall health, aiding in recovery, memory consolidation, and energy restoration. Variations in deep sleep percentages are expected as one progresses through different age stages.
For infants and young children, a significant portion of their sleep is dedicated to deep sleep. Infants, typically, can spend about 50% of their sleep time in the deep sleep stage, which is essential for their development. As children grow, the percentage of deep sleep decreases but remains substantial for their growth and development needs.
By the time an individual reaches adulthood, the deep sleep percentage narrows down to about 20-25% of total sleep. This reduction continues with age, with older adults often experiencing even less deep sleep. It’s notable that lifestyle, health conditions, and stress levels can further influence these percentages, making it imperative for individuals to monitor and adapt their sleep habits accordingly.
How to Measure Your Deep Sleep
Measuring your deep sleep is crucial for understanding the quality of rest you’re receiving each night. Various methods and tools can help you track this essential phase of sleep, which is critical for physical and mental restoration. Whether through wearable technology or professional assessments, getting insights into your deep sleep duration and quality can lead to better sleep hygiene and overall health.
One of the most popular and accessible ways to measure deep sleep is through the use of wearable sleep trackers. Devices like smartwatches and fitness bands come equipped with sensors designed to monitor movements, heart rate, and even oxygen levels while you sleep. These trackers use algorithms to estimate sleep stages, including light, REM, and deep sleep, providing you with a detailed analysis of your sleep patterns.
In addition to wearable technology, smartphone apps dedicated to sleep monitoring offer another convenient option for measuring deep sleep. Many of these apps use the phone’s accelerometer to detect movement in bed, approximating sleep stages with varying degrees of accuracy. While not as precise as wearable devices, they can still offer valuable insights for individuals looking to improve their sleep quality.
Sources of Measurement Error
However, it’s important to acknowledge the potential sources of measurement error with these tools. Factors such as device sensitivity, user behavior, and environmental conditions can affect the accuracy of sleep stage estimations. Therefore, while these methods provide a good starting point for measuring deep sleep, they should be used judiciously and, when possible, complemented with professional sleep assessments for the most accurate evaluation.
Factors That Can Influence Your Deep Sleep Percentage
Understanding the factors that can influence your deep sleep percentage is essential for improving the quality of your rest. Deep sleep, or slow-wave sleep, is crucial for your body’s recovery processes, playing a key role in memory consolidation, hormone regulation, and physical rejuvenation. Various elements, ranging from lifestyle choices to environmental conditions, can significantly impact the depth and quality of your sleep.
Lifestyle Choices and Habits
Your daily routines and behaviors have a profound impact on how well you transition into deep sleep phases. Consuming caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime can severely impair your ability to reach deep sleep. Engaging in stimulating activities, such as exercise or screen time on phones or computers, right before bed can also disrupt your sleep cycle. Conversely, establishing a calming pre-sleep routine can enhance your body’s readiness for deep sleep.
Environmental Factors
The environment in which you sleep plays a non-negligible role in dictating your sleep quality. Factors such as room temperature, noise levels, and light exposure can all influence your ability to fall into and maintain deep sleep. Ideally, your sleeping environment should be cool, quiet, and dark. Even small adjustments, like using blackout curtains or setting your thermostat to a cooler temperature, can make a substantial difference in promoting deeper sleep.
Improving Your Deep Sleep: Effective Strategies and Tips
Obtaining deep sleep is crucial for mental and physical health, rejuvenation, and overall well-being. However, many struggle to achieve consistent, restful nights. By incorporating a few effective strategies and tips, you can significantly enhance the quality of your deep sleep, leading to improved energy, mood, and health.
Establish a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Setting a calming pre-sleep ritual signals your body it’s time to wind down. Consider activities that lower stress like reading a book, practicing meditation, or taking a warm bath. Reducing screen time an hour before bed can also help decrease blue light exposure, which is known to impact sleep negatively.
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Making your bedroom conducive to deep sleep is critical. Ensure your sleeping area is cool, dark, and quiet. Investing in a high-quality mattress and pillows can provide the comfort necessary for deep sleep. Blackout curtains and white noise machines are also effective in creating an ideal sleeping ambiance.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Sleep
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a pivotal role in enhancing deep sleep. Regular physical activity, especially when done earlier in the day, can significantly improve sleep quality. Conversely, avoiding caffeine and large meals before bedtime helps prevent sleep disturbances. Prioritizing sleep hygiene by keeping a consistent sleep schedule even on weekends encourages a stable sleep rhythm, aiding in deeper sleep.
Common Misconceptions About Deep Sleep and Sleep Cycles
When it comes to understanding deep sleep and sleep cycles, there are various misconceptions that can affect how people perceive their own sleep health. One widespread myth is the notion that more deep sleep is always better. Although deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is crucial for physical recovery and memory consolidation, it’s only one part of the sleep cycle. Each stage, including light sleep and REM sleep, plays a unique role in overall health and well-being.
Another common misunderstanding is the belief that adults need less sleep as they get older. While it’s true that sleep patterns can change with age, the requirement for sleep does not drastically decrease. Adults still need 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to function optimally, but they might experience changes in how they cycle through the different stages of sleep, including deep sleep.
There’s also a misconception that if you wake up feeling tired, it means you didn’t get enough deep sleep. However, the quality of your sleep and how you cycle through the different stages is equally important. Waking up tired can be a symptom of various sleep disorders or disruptions in your sleep cycle, not necessarily a lack of deep sleep. Understanding the intricacies of sleep cycles can help debunk these myths and lead to better sleep health practices.
The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Deep Sleep Percentage
The relationship between sleep disorders and deep sleep percentage is a critical aspect to consider for anyone aiming to improve their sleep quality. Deep sleep, or slow-wave sleep, is essential for physical recovery, memory consolidation, and ensuring overall health and well-being. Various sleep disorders can significantly impact the amount of deep sleep an individual achieves, leading to a range of negative health outcomes.
Common sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome can drastically reduce the deep sleep stage. For instance, those suffering from sleep apnea experience frequent interruptions in breathing, which can repeatedly pull them out of deep sleep. As a result, individuals may wake feeling unrefreshed, despite spending an ample amount of time in bed. Similarly, insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, often leads to shortened sleep duration and a decrease in the deep sleep phase.
Moreover, the quality of deep sleep can be further compromised by factors like stress, lifestyle choices, and poor sleep hygiene. These elements can exacerbate existing sleep disorders or even create new sleep disturbances. Understanding the intricacies of how sleep disorders affect deep sleep percentage is crucial for developing effective treatment plans and lifestyle adjustments aimed at enhancing sleep quality.
No se han encontrado productos.
Deep Sleep Vs. Other Stages of Sleep: What’s The Difference?
Understanding the different stages of sleep is crucial for recognizing how deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, stands apart from the rest. Our sleep cycle consists of several stages, each playing a vital role in our health and well-being.
Characteristics of Deep Sleep
Deep sleep is the third stage in the non-REM part of our sleep cycle. It’s characterized by long, slow brain waves known as delta waves, signifying a period of deepest relaxation. During deep sleep, our body undergoes significant recovery processes – such as tissue repair, growth hormone secretion, and immune system strengthening. This stage of sleep is particularly hard to wake up from, and when disrupted, it can leave you feeling particularly groggy.
How It Differs From Other Stages
In contrast to deep sleep, the initial stages of sleep are lighter and serve as a transition into deeper sleep phases. The first stage of non-REM sleep marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep and lasts for several minutes, featuring slowing heart rate and muscle relaxation. The second stage further prepares the body for deep sleep, involving temperature regulation and decreased heart rate. Finally, REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, distinct from non-REM stages, is where dreaming occurs, and brain activity ramps up, closely resembling wakefulness.
FAQs: Answering Your Questions About Deep Sleep and Normal Ranges
When it comes to understanding the intricacies of deep sleep and normal ranges, there are numerous questions that often arise. Deep sleep, a crucial phase of our sleep cycle, is essential for physical restoration, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation. But what constitutes a normal range for deep sleep, and how can you ensure you’re getting enough? Below are some commonly asked questions that shed light on this vital topic.
What Is Considered a Normal Range for Deep Sleep?
Everyone’s sleep needs are unique, but on average, adults should aim for 1 to 2 hours of deep sleep per night, which constitutes approximately 20% of the total sleep time. This range is considered optimal for most individuals to reap the restorative benefits of deep sleep. However, factors like age, lifestyle, and overall health can influence these numbers.
How Can I Tell If I’m Getting Enough Deep Sleep?
Monitoring your sleep patterns can be instrumental in determining if you’re achieving the recommended amount of deep sleep. Advances in technology, including wearable sleep trackers and smart home devices, offer detailed insights into your sleep stages, including the amount of time spent in deep sleep. Persistent fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and feeling unrested upon waking are common indicators of insufficient deep sleep.
Understanding the significance of deep sleep and recognizing the normal ranges leads to informed choices about our sleep habits. By asking the right questions and seeking answers, we empower ourselves to improve our sleep quality and, by extension, our overall health and wellbeing.