Introduction to Italy’s Elevation Map
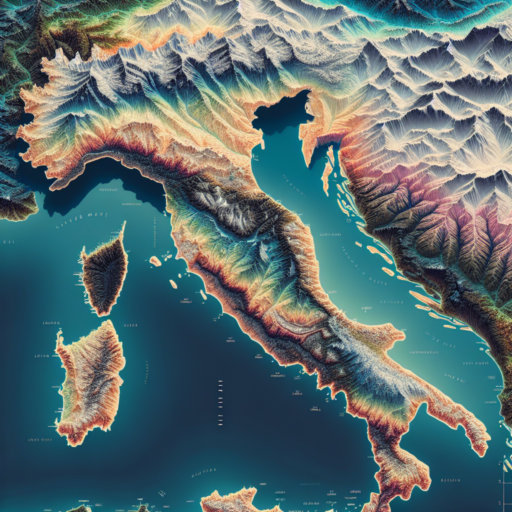
Welcome to a fascinating exploration of Italy’s elevation map, a key to unlocking the secrets of this beautifully diverse country. Italy, known for its rich history, stunning landscapes, and cultural heritage, is also a land of remarkable geographical diversity. From the soaring peaks of the Alps in the north to the gentle rolling hills of Tuscany and the rugged coastlines of the south, elevation plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s ecology, weather patterns, and human settlements.
Understanding Italy’s elevation map is essential for anyone looking to delve deeper into the geographic intricacies of the region. It reveals not just the physical contours of the country but also helps in understanding various aspects such as climate variations across different altitudes, biodiversity, and even the agricultural practices unique to specific elevation zones. The elevation map of Italy serves as a vital tool for geographers, climatologists, travelers, and those with a keen interest in landscape photography.
The Italian peninsula, characterized by its “boot” shape, is flanked by the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Seas, and is crisscrossed by a series of mountain ranges and hills that define its physical and cultural landscape. The Apennine Mountains, running down the spine of Italy, and the majestic Alps in the north, provide a dramatic backdrop to Italy’s elevation profile. These areas, along with volcanic hills and extensive coastlines, contribute to the complex elevation map that significantly influences local climates, ecosystems, and human activities.
Key Features of Italy’s Terrain As Seen on Elevation Maps
Elevation maps provide a fascinating insight into the varied terrain of Italy, highlighting areas of significant geographical interest and beauty. From the rugged peaks of the Alps in the north to the gentle rolling hills and valleys of Tuscany, each region presents a unique tapestry that has shaped the country’s culture, agriculture, and urban development.
Diverse Mountain Ranges
One of the most striking features evident on elevation maps of Italy is the presence of diverse mountain ranges. The Alps and the Dolomites dominate the northern landscape, offering some of the most breathtaking scenery in the country. These mountains not only form a natural barrier and define Italy’s borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, and Slovenia but also host a rich biodiversity and a wide range of climates.
The Apennine Mountains
Stretching like a backbone down the length of the peninsula, the Apennine Mountains are another prominent feature seen on elevation maps of Italy. These mountains influence much of Italy’s weather and are home to numerous rivers that have carved out extensive valleys and gorges over millennia. The Apennines are crucial for their hydrological resources and are a key factor in the diverse ecosystems found across the country.
Coastal Plains and Volcanic Terrain
Italy’s elevation maps also reveal a variety of coastal plains and areas of volcanic activity, which add to the dynamic nature of its topography. The Po Valley, Italy’s largest plain, plays a significant role in agriculture due to its fertile soils. Meanwhile, the volcanic areas, such as those surrounding Mount Vesuvius, Etna, and the Phlegraean Fields, are stark reminders of the powerful forces that have shaped the landscape over centuries. These volcanic sites are not only of geological interest but have also been pivotal in the development of human settlements and cultures in these regions.
Understanding the Topography of Italy Through Elevation Maps
Exploring Italy’s Varied Landscape
Italy’s distinct shape, stretching from the Alps in the north down to the southern tips of Sicily and Sardinia, offers a unique topographical diversity. Elevation maps provide an invaluable tool in visualizing the dramatic changes in landscape across the country. From the towering peaks of the Dolomites and the Apennine Range, acting as the backbone of the peninsula, to the rolling hills of Tuscany and the coastal plains, these maps reveal the intricate details of Italy’s physical geography.
The Significance of Elevation Maps in Understanding Italy’s Geography
Elevation maps are essential for comprehending the complex topographical features of Italy. They illuminate the extensive altitude ranges that characterize the country, showcasing the steep gradients of mountainous regions versus the subtle inclinations of the plains and coastal areas. Through shades of color or contour lines, these maps detail the elevations of Italy, offering insights into the geographical challenges and the natural beauty found across the Italian landscape.
Italy’s Diverse Elevations and Their Impact on Climate and Culture
The varying elevations across Italy not only shape its physical geography but also influence its climate and culture. The high altitudes of the Alps and the Apennines contribute to colder, Alpine climates, while lower areas in the Po Valley and along the Mediterranean coast enjoy milder, maritime climates. This diversity is reflected in the rich agricultural traditions, from the vineyards perched on sun-kissed hills to the arable lands of the plains. Thus, elevation maps do more than depict the land’s contours; they provide a deeper understanding of how Italy’s varied topography influences the very fabric of Italian life.
No se han encontrado productos.
Comparing Italy’s Highest and Lowest Points: Insights from Elevation Data
Exploring Italy’s geography reveals a nation of dramatic contrasts, notably when comparing its highest and lowest points. This dichotomy provides a unique lens through which to appreciate the country’s diverse landscapes and geological features. From the snow-capped peaks of the Alps to the sun-kissed shores of the Mediterranean, Italy’s elevation data uncovers fascinating insights into its natural splendor.
The Summit of the Alps: Mont Blanc
Standing at an impressive 4,809 meters (15,777 feet), Mont Blanc is not only Italy’s highest point but also the tallest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe. This colossal peak, which Italy shares with France, serves as a natural monument of the country’s towering ambition and rugged terrain. The elevation data of Mont Blanc highlights the extreme conditions and challenges that mountain climbers face, while also showcasing the breathtaking beauty and biodiversity found at such lofty heights. The mountain’s glacial fields and alpine meadows are just a few examples of the unique ecosystems that thrive in this high-elevation habitat.
The Coastal Plain: Jolanda di Savoia
Conversely, the lowest point in Italy is found at Jolanda di Savoia, a coastal plain located in the Po Valley. Situated at around -3.44 meters (-11.3 feet) below sea level, this area epitomizes the rich and fertile landscapes that characterize much of Italy’s lowlands. The extensive agriculture and navigable waterways in this region are vital to Italy’s economy and are starkly different from the alpine landscapes to the north. This contrast in elevation not only underscores Italy’s geographical diversity but also its adaptability and resilience over centuries.
Through these comparisons of Italy’s highest and lowest points, one gains a deeper appreciation for the country’s geological diversity and its influence on culture, economy, and daily life. The elevation data offers more than just numbers; it reveals stories of ecological richness, human endeavor, and the continuous interplay between the natural environment and its inhabitants.
How to Read an Italy Elevation Map: A Beginner’s Guide
Understanding how to read an elevation map, especially for a country as topographically diverse as Italy, is a crucial skill for travelers, geographers, and anyone interested in the natural landscape. Italy, with its extensive coastline, majestic mountains like the Alps and the Apennines, and iconic rolling hills in regions such as Tuscany, offers a varied elevation that is beautifully depicted in its elevation maps.
Identifying Elevation Symbols and Colors
Elevation maps use specific symbols and colors to convey information about the land’s height above sea level. In the context of Italy, you’ll notice shades of green indicating lower elevations, typically found in the Po Valley, one of Italy’s most fertile and productive areas. As you move towards higher elevations, such as the rugged Apennines that spine Italy or the majestic Alps in the north, the colors transition through tans, browns, and eventually to whites at the highest peaks, such as Mont Blanc, Italy’s tallest mountain. Recognizing these color gradients is the first step towards understanding Italy’s complex topography.
Understanding Contour Lines
Another vital component is the contour lines, which are often densely packed in areas like the Dolomites and spread wider apart in flatter regions, such as those near the Adriatic coast. Each line represents a specific elevation level, and the closer these lines are, the steeper the terrain. This is particularly noteworthy when examining areas like the Calabria region in the south, where the terrain rapidly changes from coastal lowlands to steep mountains.
Utilizing Map Legends and Scale
Lastly, always refer to the map’s legend and scale for precise understanding. Elevation maps of Italy will include a legend explaining the meaning behind various symbols, colors, and lines. The scale, usually found in a corner of the map, helps to understand the distance between points, which is essential when planning travels or studies in Italy. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, reading an Italy elevation map becomes not only an informative task but also an engaging way to explore the country’s rich geographical diversity, from the coastal regions to its highest peaks.
The Importance of Elevation Maps in Planning Your Italy Trip
When planning a trip to the beautiful landscapes of Italy, understanding the lay of the land is as crucial as knowing the weather. Elevation maps play a pivotal role in this aspect, offering insights that go beyond mere topographical interest. These maps provide valuable information on the elevation and terrain of various destinations, which is essential for a number of reasons.
Firstly, elevation maps are instrumental in planning hiking or cycling routes. Italy, with its diverse landscapes ranging from the rugged Apennines to the soaring Dolomites, offers a plethora of options for outdoor enthusiasts. By consulting elevation maps, travelers can gauge the difficulty level of different trails based on altitude changes and terrain type, ensuring a match with their physical capabilities and expectations.
Furthermore, elevation maps can also guide those interested in photography or nature sightseeing in selecting the best vantage points. The dramatic elevation changes captured in these maps hint at potential locations for breathtaking views, guiding photographers and nature lovers to those perfect spots where Italy’s scenic beauty can be fully appreciated.
In addition, elevation maps aid in understanding the climate variability within Italy. Elevation significantly influences climate, with higher altitudes offering cooler temperatures even in the heat of summer. For those looking to escape the heat or find snow-laden landscapes in winter, elevation maps serve as a crucial tool in selecting the ideal destinations for their desired experiences.
By utilizing elevation Maps in planning your Italy trip, you ensure a more informed, safe, and enriching travel experience, tailor-made to your interests and abilities.
Discover Italy’s Mountain Ranges and Volcanoes with Elevation Maps
Italy is not just a destination for history aficionados and food lovers; it is also a paradise for those attracted to its diverse and breathtaking landscapes. With its extensive coastline, picturesque lakes, and iconic mountains and volcanoes, Italy offers a blend of natural wonders that beckon to be explored. Understanding Italy’s topographical diversity is best achieved through detailed elevation maps, which reveal the intricate contours and heights of the country’s most significant geological features.
Exploring Italy’s Majestic Mountain Ranges
The Italian landscape is dominated by several mountain ranges, each with its unique allure and ecological significance. The Alps and the Dolomites in the north stand as sentinels, showcasing some of the highest peaks in Europe, marked by steep cliffs, deep valleys, and iconic spires that draw climbers and nature lovers from around the globe. Elevation maps of these areas illuminate the dramatic changes in terrain and altitude, providing a visual guide for adventurers and geologists alike. The Apennines, stretching like a spine down the length of the peninsula, offer a gentler, but no less stunning, topography of rolling hills and verdant forests, rich in biodiversity.
The Allure of Italy’s Active Volcanoes
Italy’s geological tapestry would be incomplete without the mention of its active volcanoes—Vesuvius, Etna, and Stromboli—each adding a thrilling component to the country’s landscape. Elevation maps highlight the slopes and craters of these volcanoes, offering a stark visual contrast to the surrounding terrain. These volcanic wonders not only shape the local geography but also tell a tale of ancient eruptions and the ever-present potential for future activity. Understanding their elevation and structure through maps provides invaluable information for scientists and tourists, emphasizing the dynamic nature of Italy’s land.
Utilizing elevation maps to explore Italy’s mountain ranges and volcanoes brings to light the dramatic beauty and geological complexity of the country. These maps serve as tools for education and exploration, allowing us to appreciate the high peaks and deep craters that define Italy’s landscape. The textured layers of earth, from the rugged Alps to the fiery craters of its active volcanoes, are a testament to the natural forces that have shaped this land throughout history.
Exploring Italy’s National Parks and Their Elevations
Italy, a country renowned for its rich history, exquisite cuisine, and unparalleled landscapes, is also home to an array of national parks each with its own unique elevation and ecological diversity. These parks offer a vista into the country’s vast natural beauty and provide a haven for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. From the soaring peaks of the Alps in the north to the gentle Mediterranean scrublands of the south, Italy’s national parks showcase a wealth of biodiversity and geological variety.
Gran Paradiso National Park, located in the Graian Alps, boasts the title of Italy’s first national park. Established to protect the Ibex population, this park elevates from 800 meters to an impressive 4,061 meters at the peak of Gran Paradiso itself. The variations in elevation within Gran Paradiso offer habitats to a plethora of wildlife and provide breathtaking landscapes that stretch far beyond the horizons.
Another gem is the Dolomiti Bellunesi National Park nestled in the Dolomites mountain range. Characterized by its dramatic mountain peaks which reach elevations up to 2,565 meters, this park is a UNESCO World Heritage site due to its extraordinary scenic beauty and unique geological formation. Here, the changes in altitude create a mosaic of ecosystems ranging from Alpine meadows to dense forest valleys, housing diverse species of flora and fauna.
Using Elevation Maps to Understand Climate Zones in Italy
Italy’s diverse climate zones can be intricately understood through the lens of elevation maps, providing a unique perspective on how altitude affects regional climates. From the snow-capped peaks of the Alps in the North to the warm, Mediterranean coasts in the South, Italy offers a rich tapestry of climatic conditions. Elevation maps serve as crucial tools in delineating these climate zones, offering insights into the geographical distribution of weather patterns across the country.
Elevation maps highlight the drastic changes in climate experienced at different heights. For instance, the Apennine Mountains, running down the spine of Italy, act as a barrier that influences the climatic differences between the eastern and western coasts. By studying these maps, one can observe how areas at higher elevations, like much of the Alps and the Apennines, have colder, alpine climates. In contrast, lower areas, especially those near the coast, experience warmer, Mediterranean conditions.
The application of elevation maps in understanding Italy’s climate zones is not just academic. It has practical implications for agriculture, urban planning, and tourism. By recognizing the climatic characteristics informed by altitude, stakeholders can make informed decisions that align with the environmental conditions of their specific locales. This knowledge is vital for predicting weather patterns, preparing for climate-related challenges, and optimizing land use to suit various activities.
Interactive Italy Elevation Maps: Tools and Resources
Exploring Italy’s diverse landscape is a fascinating endeavor, and interactive Italy elevation maps provide an immersive way to understand the contours and topography of this beautiful country. These digital tools have revolutionized how both tourists and researchers explore regions, from the towering Alps in the north to the rugged coastlines of the south. By leveraging detailed elevation data, users can plan hikes, research geographical phenomena, or simply marvel at Italy’s natural beauty from the comfort of their own homes.
The availability of various tools and resources makes accessing these interactive maps easier than ever. Online platforms offer user-friendly interfaces that cater to both professional geologists and casual nature enthusiasts alike. These maps often include layers that can display not just elevation, but also historical sites, hiking trails, and even live weather patterns, providing a comprehensive overview of Italy’s geography. The sophistication of these tools allows for a close-up view of specific areas, making it possible to zoom in to see the elevation of iconic locations like Mount Etna or the rolling hills of Tuscany in precise detail.
Advancements in technology have been key in enhancing the accuracy and accessibility of these elevation maps. High-definition satellite images and cutting-edge GIS (Geographic Information System) technology combine to offer a dynamic and interactive experience. Users can now switch between different types of map views, such as topographic, satellite, or a hybrid of both, ensuring that they get the most informative view that suits their needs. This technological evolution not only bolsters the experience of the end-user but also supports academic research and environmental monitoring efforts across Italy.