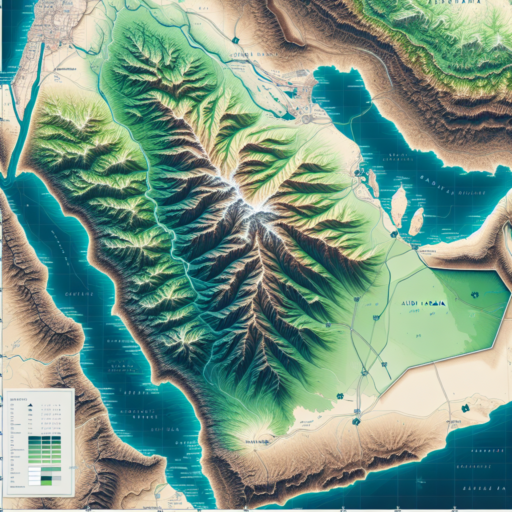
Introduction to Saudi Arabia’s Topography
Saudi Arabia, a country known for its vast deserts and long coastlines, possesses a unique and diverse topography that shapes its geography and cultural identity. This landscape ranges from mountain ranges and sandy dunes to rocky plains and fertile valleys, each playing a crucial role in the kingdom’s ecosystem and human activities.
At the heart of the country lies the Arabian Desert, a vast expanse of sandy terrain that has captivated travelers and explorers for centuries. However, Saudi Arabia’s topography is not monolithic. The southwestern region, for instance, is dominated by the Asir Mountains, which include the kingdom’s highest peak, Jabal Sawda. These mountains not only influence the local climate by attracting higher rainfall but also host a surprising diversity of flora and fauna.
Beyond the mountains and deserts, the country’s topography is punctuated by its extensive coastlines along the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf. These coastal areas are crucial for the country’s economy, harboring major ports and driving the fishing industry. Additionally, the coastal plains and islands support unique ecosystems and offer some of the most stunning landscapes in Saudi Arabia.
Key Features of the Saudi Arabian Topographic Map
The topographic map of Saudi Arabia is an essential tool for various professionals and enthusiasts, offering a detailed representation of the country’s geographical features. This map is intricately designed, shedding light on the complex physical landscape of this vast nation. From the stretching deserts to the majestic mountains, every aspect of the terrain is captured with remarkable accuracy. Understanding these key features can significantly enhance one’s comprehension of the country’s geography and its natural resources.
Detailed Elevation Contours
One of the most significant features of the Saudi Arabian topographic map is its detailed elevation contours. These contours provide a clear and precise depiction of the elevation changes across the country. Such detail is invaluable for geologists, climbers, and construction engineers, as it aids in planning and navigation. The contours are meticulously drawn, offering insights into the heights of the Empty Quarter’s sand dunes as well as the peaks of the Asir Mountains.
Extensive Hydrographic Data
Another crucial aspect of the topographic map is its extensive hydrographic data. This includes detailed representations of water bodies such as the Red Sea coastline, rivers, wadis, and even small lakes and ponds. Hydrographic data is essential for environmental researchers, urban planners, and water resource managers, providing them with the necessary information to make informed decisions about water conservation and land development.
Comprehensive Road Networks and Urban Areas
The map also features comprehensive road networks and urban areas, offering a bird’s-eye view of Saudi Arabia’s vast infrastructure. Major highways, rural roads, and city streets are all clearly marked, alongside urban areas from bustling cities like Riyadh and Jeddah to remote villages. This feature aids travelers, logistic companies, and government agencies in planning and development activities, ensuring a thorough understanding of accessibility and connectivity across the country.
Understanding Elevations: Mountains and Deserts in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is a land of contrasting landscapes, where the majestic mountains and sprawling deserts form the backbone of the region’s geographical identity. This diverse topography not only shapes the country’s climate and natural habitats but also tells a story of geological events spanning millions of years. Understanding the elevations of these features is key to appreciating the natural beauty and ecological significance of the region.
The mountains in Saudi Arabia, such as the Asir and Hejaz ranges, are predominantly located in the western part of the country. These mountain ranges are notable for their breathtaking peaks, with some rising above 2,500 meters. The elevations of these mountains profoundly influence the local climate, contributing to cooler temperatures and higher precipitation levels than the surrounding deserts. This climatic difference makes the mountainous regions a biodiversity hotspot, supporting a variety of flora and fauna that cannot be found elsewhere in Saudi Arabia.
Contrastingly, the deserts of Saudi Arabia, including the vast Rub’ al Khali or the «Empty Quarter,» embody a different aspect of the country’s elevations. The Rub’ al Khali, one of the largest sand deserts in the world, features an extraordinary landscape of dunes, some reaching heights of up to 250 meters. Despite the harsh conditions, these desert elevations harbor a unique ecosystem adapted to survive in extreme temperatures and scarcity of water. The interplay between the high mountains and expansive deserts of Saudi Arabia is a testament to the country’s ecological diversity and geological history.
How to Read a Topographic Map of Saudi Arabia
Understanding the intricate details of a topographic map, especially of a region as vast and diverse as Saudi Arabia, is essential for travelers, researchers, and enthusiasts of geography alike. Topographic maps offer more than just road routes; they provide a detailed view of the terrain’s physical features, including mountains, valleys, and plains. This makes them particularly valuable for planning hikes, geological surveys, and educational purposes.
Identifying Key Symbols and Colors
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols and colors to represent different physical features and elevations. For instance, brown lines, often called contour lines, indicate elevation and the shape of the terrain. The closer these lines are, the steeper the terrain is. Other symbols may denote specific landforms such as sand dunes in desert areas, prevalent in much of Saudi Arabia, or wadis, which are dry riverbeds that can flood during rainstorms. Recognizing these symbols is crucial for understanding the geographical layout of the area.
Understanding Scale and Contour Intervals
The scale of the map is fundamental in reading and interpreting distances accurately. Topographic maps of Saudi Arabia might come in various scales, but ones with a 1:100,000 scale are commonly used for detailed study and navigation. This means that 1 centimeter on the map equals 1 kilometer on the ground. Additionally, the contour interval, or the vertical space between contour lines, gives you insight into the gradient of the terrain. A smaller interval suggests a gentler slope, whereas a larger interval indicates a steep climb or descent.
By mastering these elements—symbols, colors, scale, and contour intervals—you can effectively navigate and appreciate the rich topographical diversity of Saudi Arabia. Whether it’s planning a route through the Asir Mountains, exploring the vast Rub’ al Khali desert, or simply understanding the country’s geography, a topographic map is an invaluable tool.
No se han encontrado productos.
Top 5 Uses for a Saudi Arabian Topographic Map
A Saudi Arabian topographic map is not just a representation of the country’s terrain; it’s a versatile tool with a variety of applications. These maps, with their detailed contour lines and geographical features, serve purposes that range from academic research to adventurous excursions. Below, we explore the five primary ways in which a topographic map of Saudi Arabia proves invaluable.
Navigational Aid for Outdoor Activities
One of the most classic applications of a Saudi Arabian topographic map is for navigating the country’s vast and varied landscapes. Whether it’s for hiking the Sarawat Mountains, exploring the Rub’ al Khali desert, or enjoying the beauty of the Red Sea coast, these maps provide detailed information about the terrain, elevations, and pathways, making them indispensable for outdoor enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
Environmental Research and Conservation
Topographic maps are crucial for environmental scientists and conservationists. In a country like Saudi Arabia, where diverse ecosystems from deserts to marine habitats exist, these maps offer insights into land forms, drainage systems, and habitat distribution. They are essential tools in environmental impact assessments, conservation planning, and in the management of natural resources, helping to balance development with ecological preservation.
Urban Planning and Development
As Saudi Arabia continues to grow and modernize its infrastructure, topographic maps play a fundamental role in urban planning and development. These maps provide planners and engineers with the detailed topographical information necessary for designing roads, bridges, and buildings, ensuring that developments are sustainable and in harmony with the natural terrain. This is particularly important for projects in challenging landscapes, such as the construction of Neom, the new futuristic mega-city.
Exploring Saudi Arabia: Major Geographic Regions Highlighted
The geographical tapestry of Saudi Arabia is as diverse as it is expansive, encompassing a range of landscapes from deserts to mountain ranges. This variation not only contributes to the country’s physical beauty but also to its rich cultural heritage and economic resources. In an exploration of Saudi Arabia’s major geographic regions, a few areas stand out, each lending a unique hue to the country’s vibrant palette.
The Arabian Desert: The Heart of the Peninsula
Occupying the lion’s share of the Arabian Peninsula, the Arabian Desert is an expansive sea of sand that has shaped the cultural and economic landscape of the region. It is the classic image of Saudi Arabia, with its rolling sand dunes and oases providing respite to travelers for millennia. This vast desert is also home to the Rub’ al Khali or the Empty Quarter, the largest continuous sand desert in the world, highlighting the extreme conditions that have influenced the resilient cultures of the Arabian Peninsula.
The Hejaz Region: A Cultural and Religious Hub
Bordering the Red Sea to the west, the Hejaz region is of great religious and historical significance. It is home to Islam’s two holiest cities, Mecca and Medina, drawing millions of pilgrims annually. Beyond its religious importance, the Hejaz features diverse geography, from the coastal plain along the Red Sea to the majestic Sarawat Mountains, offering captivating landscapes and a climate that diverges dramatically from the desert interior.
The Asir Region: Nature’s Bounty
Contrasting with the arid landscapes that characterize much of Saudi Arabia, the Asir region boasts lush mountains and fertile plains, thanks to its higher elevation and proximity to the Red Sea. This results in a cooler climate and more verdant scenery, providing a backdrop to some of Saudi Arabia’s most unique biodiversity. The area also supports agriculture, contributing to the country’s food supply and offering a scenic escape for both locals and tourists seeking a retreat from the desert heat.
The Importance of Topographic Maps in Environmental Studies and Planning in Saudi Arabia
Topographic maps play an indispensable role in environmental studies and planning, especially within the context of Saudi Arabia’s unique geographical layout. These maps, by detailing the physical features of the land, provide a crucial foundation for understanding the environmental dynamics and planning sustainable development projects. The Kingdom’s vast deserts, imposing mountain ranges, and varied coastline are all intricately documented through topographic mapping, enabling a comprehensive analysis of its ecological and urban challenges.
Topographic maps are essential in identifying potential environmental risks and opportunities in Saudi Arabia. For instance, they assist in water resource management by depicting catchment areas, drainage patterns, and aquifer locations, which is critical for addressing the country’s water scarcity issues. Similarly, these maps facilitate the planning of infrastructural projects by ensuring that developments are compatible with the land’s natural contours and minimize environmental degradation.
Key Applications of Topographic Maps in Saudi Environmental Planning
- Risk Assessment: By highlighting flood plains, fault lines, and areas prone to erosion, topographic maps aid in mitigating natural disaster risks.
- Conservation Efforts: They help in delineating protected areas and in the planning of biodiversity conservation projects, ensuring that Saudi Arabia’s unique habitats are preserved for future generations.
- Urban Planning: Topographic maps are instrumental in the thoughtful expansion of cities and towns, blending human habitation seamlessly with the natural environment.
Where to Find the Most Accurate Saudi Arabia Topographic Map
Finding the most accurate topographic map of Saudi Arabia is essential for a variety of professionals, from geologists and urban planners to adventurers seeking to explore the vast landscapes of this desert kingdom. Thankfully, there are several reliable sources where one can find detailed and up-to-date topographic maps that cover this extensive area. Each source varies in the type of data provided, level of detail, and accessibility, making it crucial to choose the right one for your specific needs.
Online Geographic Information System (GIS) Platforms
One of the most accessible ways to obtain accurate topographic maps of Saudi Arabia is through online GIS platforms. These websites host a wealth of geographic data and allow users to view, download, or even customize maps. Platforms such as the Saudi Geological Survey (SGS) and the Global Environmental Facility are renowned for their comprehensive databases, offering high-resolution maps that include contour lines, elevations, and detailed terrain features. The convenience of accessing these maps from any device with an internet connection makes online GIS platforms a first stop for many professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Academic and Research Institutions
For those who require maps with specialized data or extreme precision, academic and research institutions are invaluable resources. Universities with geography or earth sciences departments often have extensive collections of topographic maps, including those of Saudi Arabia. Additionally, collaborations between Saudi Arabian universities and international research organizations can yield unique topographic maps that are not readily available elsewhere. These resources are particularly useful for scholarly research that demands the highest level of accuracy and detail.
Regardless of whether you’re planning a rigorous scientific expedition or simply looking to explore the breathtaking landscapes of Saudi Arabia, having a reliable topographic map is crucial. By consulting the right sources, such as online GIS platforms and academic institutions, you can ensure that your map is not only accurate but also tailored to your specific requirements. The journey to find the perfect topographic map might seem daunting, but it’s an essential step in unlocking the full potential of your endeavors in Saudi Arabia.
Navigating Through Saudi Arabia: A Topographic Perspective
Saudi Arabia, a vast kingdom in the Arabian Peninsula, offers an intriguing mix of flat desert terrains and striking mountain ranges. Understanding the topographic variations across the country is essential for anyone looking to explore or navigate through its expanses. From the Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter) in the south, which stands as the largest contiguous sand desert in the world, to the soaring heights of the Sarawat Mountains, the country presents a complex landscape that demands attention.
The coastal plains, such as the Tihama on the Red Sea, contrast sharply with the country’s interior plateaus. These regions are not only geographically diverse but also impact the climate, making navigation and planning critical for travelers. Highlighting the importance of a topographic perspective allows for a deeper understanding and appreciation of Saudi Arabia’s natural beauty and challenges posed by its terrain.
Moreover, the transition from urban landscapes to the natural topography presents a unique challenge for navigation. Cities like Riyadh, located on the Najd plateau, demonstrate how urbanization integrates with the natural topography. Navigating through Saudi Arabia, thus, involves an awareness of both the constructed and natural elements that define its land.
Comparing Historic and Modern Topographic Maps of Saudi Arabia
Understanding the changing landscapes of Saudi Arabia requires a closer examination of both historic and modern topographic maps. These maps serve as a dynamic testimony to the intricate shifts in geography, urbanization, and natural features over time. By comparing these maps, one can gain profound insights into how the regions within Saudi Arabia have evolved, mirroring the nation’s economic growth, technological advancements, and conservation efforts.
Evolution of Mapping Techniques
The methodology and precision in creating topographic maps have seen considerable advancements. Historic maps of Saudi Arabia were often crafted through ground surveys and observations, relying heavily on physical landmarks and manual measurements. In contrast, modern topographic maps utilize satellite imagery, GPS data, and digital elevation models. This transition has not only improved the accuracy of maps but also the speed at which they can be updated, offering a more detailed and current representation of the terrain.
Impact on Urban and Rural Development
Comparison of these maps highlight the profound impact of urbanization in Saudi Arabia. With the discovery of oil and the subsequent economic boom, cities like Riyadh and Jeddah have witnessed exponential growth. This is vividly captured in modern topographic maps that show dense urban infrastructure compared to more sparse representations on historic maps. Moreover, the development of new roads, industrial areas, and agricultural projects are clearly depicted, indicating shifts in land use patterns and the expansion of urban areas into what was once predominantly desert terrain.
Through the lens of topographic maps, the contrast between Saudi Arabia’s past and present becomes strikingly clear. These maps offer invaluable insights into the environmental, economic, and social transformations that have shaped the kingdom. By comparing the detailed contours, scales, and features of historic and modern maps, one can appreciate the complexity of these changes and the continued evolution of Saudi Arabia’s landscape.