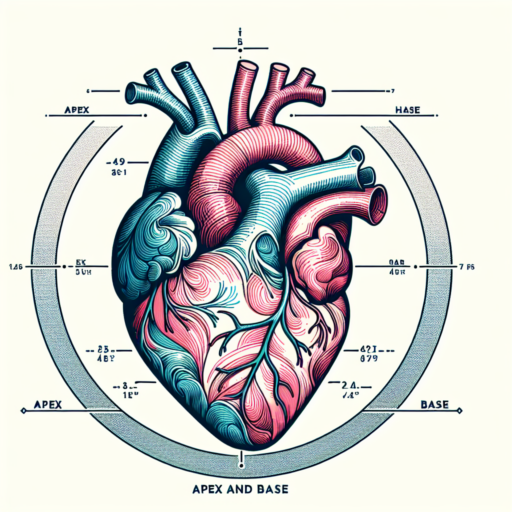
What is apex and base of the heart?
Understanding the anatomy of the heart is crucial for comprehending how this vital organ functions. Two fundamental terms often encountered when discussing heart anatomy are the «apex» and the «base» of the heart. These terms represent specific areas that play significant roles in the heart’s overall operation and its interaction with the circulatory system.
The apex of the heart refers to the lower, pointed end of the heart that extends slightly to the left. It is positioned just above the diaphragm, pointing downwards, forwards, and to the left. The significance of the apex lies in its role in the heartbeat; it is where the heart’s contractions begin, pushing the blood into the systemic circulation. This area is also where one can feel the heart’s pulsations most strongly, typically detected in the fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line.
On the other hand, the base of the heart is located at the heart’s top, opposite the apex. It is primarily formed by the left atrium, and partially by the right atrium, facing upwards, backwards, and to the right, adjoining the great vessels of the heart – the aorta, pulmonary arteries, and veins, and the superior and inferior vena cava. The base’s primary function is to facilitate the flow of blood to and from the heart, acting as a crucial junction between the heart and the systemic as well as pulmonary circulations.
Understanding the specific locations and functions of the apex and base of the heart is key to grasping the heart’s intricate operations. These regions are pivotal in ensuring the effective pumping and circulation of blood throughout the body, highlighting the heart’s essential role in our overall health and wellbeing.
What is the difference between base and apex?
Understanding the difference between the base and the apex is crucial in various fields such as geometry, biology, and architecture. In a general sense, the base refers to the bottom or support of an object, structure, or figure, upon which it stands or lays. Conversely, the apex is the highest point or tip of something, often pointing upwards in contrast to the base’s position. These terms help in identifying and describing the orientation, structure, and components of objects and systems in a clear and succinct manner.
In geometry, for instance, the base of a triangle or pyramid is the side or face upon which the figure is perceived to stand. This is where calculations such as area and volume often begin. The apex in geometric terms is the vertex opposite the base, especially in pyramids or cones, representing the peak or culmination point. This geometric relationship between base and apex is essential in understanding shapes, their properties, and their spatial orientations.
In the realm of biology, the terminology shifts to describe structures of organisms. The base can refer to the broader part of an organ from which it grows, like the base of a leaf stem connecting to the plant’s main body. The apex in biological contexts often describes the tip end of an organ, such as the apex of the heart, pointing downwards and to the left of the human body. This distinction is vital in discussing anatomy, growth patterns, and functions of biological entities.
What is the base of the heart called?
The base of the heart is a crucial anatomical component integral to its structure and function. Often described as the heart’s uppermost surface, this key area lies directly opposite the apex of the heart, which is more pointed and positioned towards the lower body. The base is primarily known for its role as a site where major blood vessels enter and exit the heart. These include the pulmonary veins, the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava, as well as the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Located towards the back and upper part of the heart, the base is primarily formed by the left atrium and, to a lesser extent, by part of the right atrium. This part of the heart plays an essential role in the cardiac cycle, especially in the effective circulation of blood throughout the body. By facilitating the entry and exit points for blood, the base of the heart ensures efficient oxygenation of blood by distributing oxygen-rich blood to various parts of the body while also receiving deoxygenated blood for purification.
In medical terminology, the significance of the heart’s base extends beyond its structural components and into its functional importance in both circulatory and respiratory systems. Understanding the anatomy of the heart’s base is vital for healthcare professionals, as anomalies or dysfunctions in this area can lead to significant cardiovascular conditions. The health of the heart’s base is often a focal point in diagnostic processes, highlighting its importance in overall cardiac health.
No se han encontrado productos.
Which chamber is the apex the bottom of?
The heart’s structure is fascinating and complex, playing a crucial role in our body’s circulatory system. One common question that arises when studying the anatomy of the heart is about its chambers and specifically, regarding the apex. The apex is an integral part of the heart’s anatomy, providing crucial insights into how this vital organ functions.
Located at the bottom tip of the heart, the apex is primarily formed by the left ventricle. This positioning is key to understanding the heart’s pumping mechanism. The left ventricle’s pivotal role in pumping oxygenated blood through the aorta to the rest of the body highlights the importance of the apex in the heart’s overall anatomy and function. This bottom positioning of the apex allows for a more efficient pumping action, given the gravitational support and the natural shape of the heart.
It’s interesting to note that the apex’s position can vary among individuals depending on several factors, including the shape and size of the heart, overall health, and even the body’s position. Despite these variations, the apex consistently remains an essential part of the left ventricle. Its position and function are critical for the effective circulatory operation within the human body, underscoring the interconnectedness of heart anatomy and its vital role in our health and well-being.